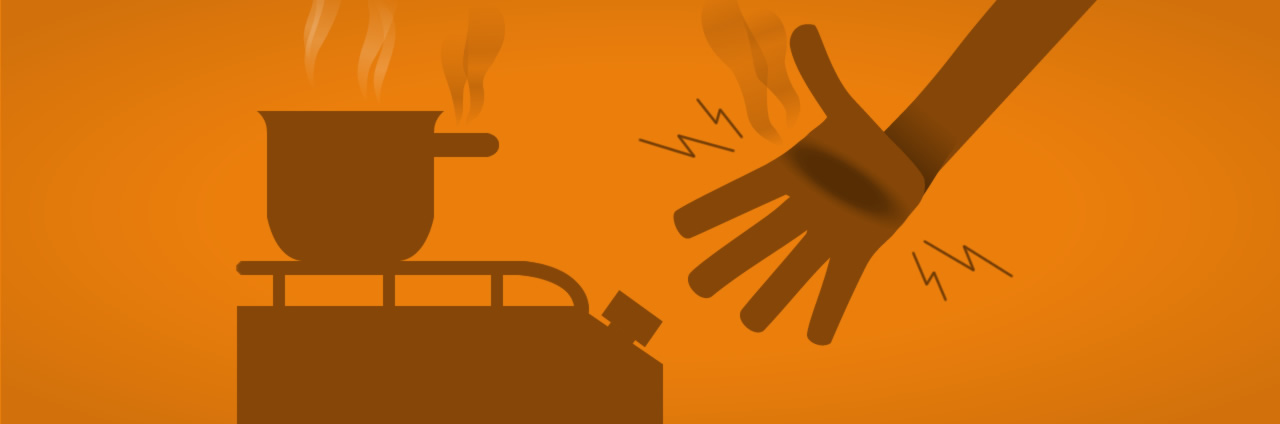
Burns: no one likes heat
Burns are not only caused by heat. Corrosive chemicals such as caustic soda and hydrochloric acid, and also sunshine, can also burn the skin. Their severity depends on the size of the injury, which part of the body is affected, and how it is caused.
Burns are tissue lesions caused by contact with high temperatures or corrosive substances. They have different origins and degrees of severity, and may be caused by such things as flames, incandescent metal, boiling water, and contact with corrosive substances like caustic soda and hydrochloric acid. They can also be caused by sunlight, in which case the degree of burning will depend on the length of uncontrolled exposure.
Burns: it's all a question of size
The severity of a burn depends first of all on its size, which part of the body is affected, and its cause. For example a small third-degree burn is not life threatening, whereas a very large second-degree one can have a more serious prognosis.
Burns: the map of the most delicate areas
The severity of a burn may also depend on the area affected by the lesion. For example, it is important to know whether it is located on a joint, or an area of skin that is subject to stretching or otherwise delicate, such as the neck or face. Burns to the face, eyes, ears and genitals must always be assessed by a specialist.
Burns: the importance of heat
Other factors affecting the severity of a burn are the type of object that caused it, and its specific temperature. Generally speaking, burns caused by corrosive substances are more extensive. Those resulting from caustic products such as hydrochloric acid are always considered to be serious, regardless of their size.
The severity of a burn also depends on time
It is easy to assess the effect of exposure time on the severity of a burn. Some first-degree burns, which have less serious consequences, may be caused by contact with an object with a temperature of 45 degrees for 6 consecutive hours. But an equally severe burn may be caused by 2 minutes of contact with an object at 51 degrees, or a single second at 60 degrees. One second's contact with an object at 65 degrees can cause a second-degree burn.
Talking about sunburn
Burns are injuries to the skin caused by exposure to heat, including the sun. As with other types of burns, the severity of sunburn depends on the depth and extent of the affected area. The bigger the burn, the more capillaries will be damaged. Sunburn can also cause dangerous dehydration if more than 15% of the total skin surface is affected in adults, or 10% in children.